All you need to know about the window’s energy performance

The label on an energy-rated window is a product declaration of its energy performance. It contains information that can help you in calculating the house’s energy requirement as well as its energy balance – i.e. the supply of free solar energy, heat losses and any need for comfort cooling. Below is a summary of the content.
Read more about the manufacturers
Under FIND MANUFACTURERS are links to manufacturers of energy-rated windows. The website of the relevant company contains more information about which windows are energy-rated.
Every window is unique
When a window is fitted with different glass or edge spaces, its U-value, g-value and LT-value change. This is why the label only applies to exactly the same design with the same glazing combination as specified in the certificate.
Energy classes from A to G
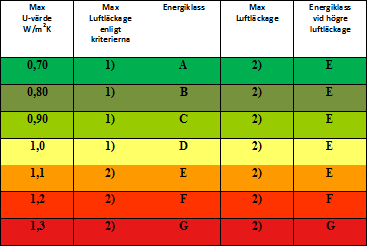
Energy classes A–G are based on the window’s U-value and on how air-tight the window is. The maximum permissible air permeability at reference pressure 100 Pa (pascals) is:
Class A–D (Q100) 1 m³/h, m²
Class E–G (Q100) 3 m³/h, m²
Example: If the window has a U-value of 0.7 and maximum permeability is 1 m³/h, m², it is allocated energy class A, but if permeability exceeds this, it is placed in energy class E.
All energy-rated windows in classes A–F are designated energy-efficient. A double-glazed window with ordinary glass has a U-value of approximately 3.0 W/m2K, and a triple-glazed window with ordinary glass has a U-value of approximately 2.0 W/m2K. An A-rated window is three times better than a triple-glazed window with ordinary glass and four times better than a double-glazed window with ordinary glass.
The U-value indicates the insulating capacity
A window’s U-value is a measurement of heat losses through the window, the unit of measurement being W/m2K.
Note that the U-value applies to the entire window, i.e. the combination of glazing, frame and sash together. The lower the U-value, the better the window insulates. Since the purpose of energy rating is to enable rapid comparisons of windows from different manufacturers, the U-value is based on a reference dimension laid down in the European standard for windows: 1230 x 1480 mm.
The LT-value specifies the amount of daylight
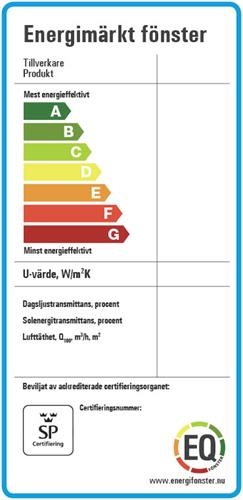
Daylight transmittance is specified in percent and is a measure of the amount of daylight that enters through the window. An LT-value of around 60% gives good daylight conditions. In residential dwellings, as high an LT-value as possible is usually desirable, particularly if the dwelling has few windows and these are of small dimensions. In workplaces, a high value can cause glare, particularly when working at a computer. It is a good idea to seek expert help in order to simulate and optimise the daylight in workplaces or for other larger projects.
The g-value relates to solar radiation
The g-value specifies how much solar radiation enters through the window. High solar transmittance means that a lot of free heat enters the building.
However, in rooms with large areas of glazing (particularly south- and west-facing), a low g-value may be beneficial. There will of course be less free energy, but the room will be cooler and more pleasant when the sun is shining. Low-emissivity (energy-saving) and colour-neutral solar control glass may be an option in such cases. In schools and workplaces where people, lighting and machines give off a lot of heat, windows fitted with solar control glass are almost always preferable.
Air permeability (air tightness) in four classes
The air permeability or air tightness of a window is tested in laboratories in accordance with European standard EN 12207. This standard specifies four classes. Windows in class 1 may leak 50 m3 of air per hour per m2 of window area at a pressure of 100 Pa (pascals). In class 4, maximum permeability of the window must not exceed 3 m3 of air per hour per m2 of window area.
Air tightness is an essential characteristic of a window’s total energy efficiency. For this reason, EQ rating and labelling for energy classes A to D requires maximum air permeability of 1 m³ of air per hour/m². It corresponds to only 1/3 of the amount permitted by the most stringent class as defined in EN 12207. It is 50 times less than that permitted by class 1 of the standard – see table.
Accredited certification body
Because the energy rating is awarded exclusively by a certification body accredited by Swedac, you can rely on the information provided on the energy label.